Second quarter results for Tesla are out, but are they convincing enough to reflect the company’s continued success. The company’s Q2’2024 sales of $25.5 bn, surpassed the Bloomberg consensus estimates of $24.63 bn, and also slightly elevated compared to the $24.9 bn in Q2’2023.
While the results were not entirely bad, they certainly seem deceptive hiding the real pain that the carmaker has been grappling with over the last few months. The company’s core business, of EVs, is struggling, as reflected by its recent quarterly results. The automotive sales segment in Q2’2024 experienced a decline of 9.3% Y-o-Y, while H1’2024 sales were down 11% Y-o-Y. Additionally, consumer car vehicles production dropped by 14% in Q2’2024, compared to previous year. This decline in the production could potentially translate to weak car sales in the rest of 2024.
Furthermore, Tesla’s Q2’2024 net income plummeted by 45% Y-o-Y, as the company’s global electric vehicle sales tumbled despite efforts towards price reductions and low-interest financing. Notably, Tesla began offering a 5 year interest free loan, to spur sales of its EVs in China in April 2024. Similarly, the company rolled out 0% financing over a 4-year period for buyers of the new Model Y Long Range All-Wheel Drive in Germany, purchased during the quarter. The company’s expenditures are rising due to investments in AI infrastructure essential for transforming Tesla EVs into autonomous vehicles and for the development of humanoid robots.
Table of Contents
What Exactly Contributed to the Marginal Increase in Tesla Sales?
Tesla’s overall revenue rose 2.3% Y-o-Y to $25.5 bn in Q2’24, fuelled primarily by “Energy generation and storage”, along with “Automotive regulatory credits” segment. The energy sector witnessed over 100% growth as more residences and businesses embraced solar power generation and storage; while regulatory credit income surged by over 200% due to other electric vehicle manufacturers lagging in meeting low carbon emission standards. Growth in these segments is good, however they collectively account for only 15% of the total revenue, and thus are insufficient to sustain longer-term growth for the company.
What Factors Are Leading to the Decline in Tesla’s Automotive Segment?
The decline in the Automotive segment raises concerns about what this trend signifies for investors. Tesla’s sales are on a downward trajectory, prompting a closer examination in relation to its counterparts in the electric vehicle industry. In the US, the company has been a bellwether in the electric vehicle sector over the past few years. In the 12 months through May 2024, the company sold approximately 618,000 electric cars in the US, compared with about 597,000 fully electric vehicles sold by other manufacturers, according to Marklines, a provider of monthly auto industry sales data.
Nevertheless, with the emergence of new competitors in the U.S. market, Tesla appears to be at risk of relinquishing its longstanding dominant position, where it previously outsold all other electric vehicle competitors combined. This shift is evident in the diminishing gap between Tesla’s sales and those of other electric vehicle players collectively.
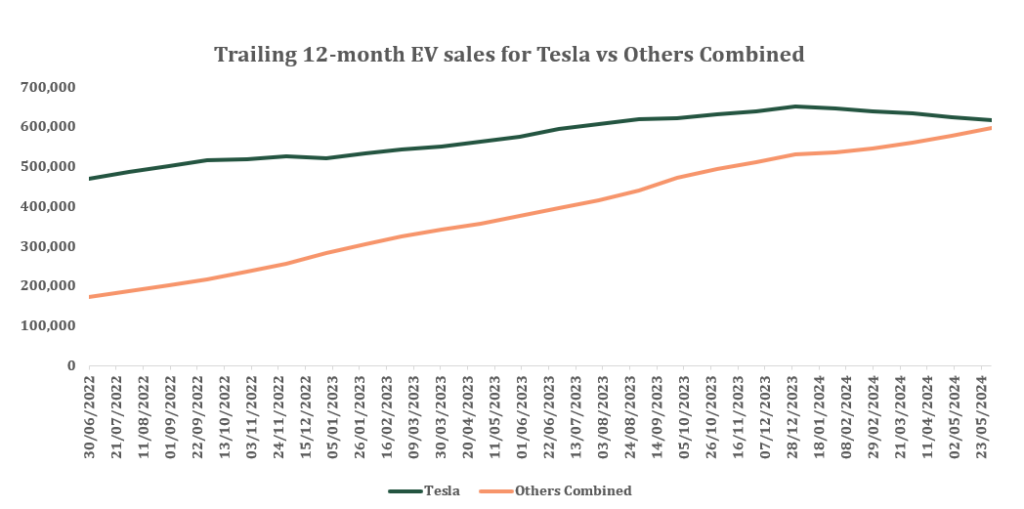
As per Stephanie Valdez-Streaty, director at Cox Automotive, “Tesla just has a lot more competition now, Elon really moved the industry forward with electrification, but he’s trying to compete against other brands with new models out — and Tesla doesn’t have any new models.”
Tesla has maintained its position as the leading electric vehicle seller in the US. since its Model S luxury sedan surpassed the Nissan Leaf in 2015, and it has consistently outsold the entire industry combined since the popularity of the Model 3 began in 2018. Nonetheless, traditional automakers have gradually started to emerge and narrow the gap. In the second quarter of 2024, Tesla’s automotive segment experienced a 13% year-on-year decline in sales, causing ripples of concern in the U.S. market, especially as the sales of its two primary competitors, Hyundai/Kia and Ford, surged by 56% and 86% respectively Y-o-Y.
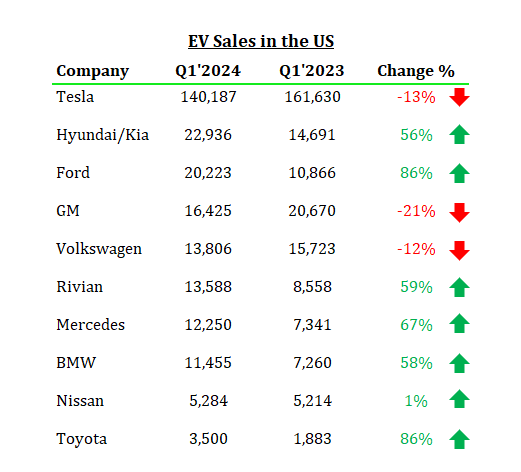
Hyundai is accelerating its efforts to close the gap with Tesla in the US electric vehicle market. The company is on the track to finish the construction of its first EV and battery plant – Hyundai Motor Group Metaplant America (HMGMA), located in Georgia, by the end of 2024. Similarly, the traditional automaker Ford also plans to spend $50 billion on EV models through 2026 and is hoping to produce 2 million EVs annually by that time. In 2023, Ford sold 72,608 EVs in the U.S., second highest seller after Tesla, with an 18% year on year increase.
Tesla also faces a strong competition from China, the world’s largest automotive market. By 2023, approximately 123 automakers in China were actively involved in selling electric vehicles, many of which benefited from substantial subsidies from Beijing. In the domestic arena, automakers are grappling with a fierce price competition, spearheaded by BYD, Tesla’s primary rival, leading to a deceleration in EV sales growth. Simultaneously, they are eyeing international markets, notably in Europe, Asia, and Oceania, by amping up EV exports and flooding these regions with competitively priced vehicles.
What Lies Ahead for the Electric Car Market?
As per IEA, the global electric car sales surged 35% Y-o-Y in 2023, to almost 14 million. EVs are poised to play a pivotal role in the ambitious target of achieving zero-emissions by 2050, driving significant industry preparations. The market is expanding rapidly and universally.
Projections by Goldman Sachs indicate that electric vehicles will make up approximately 35% of all new car sales worldwide by 2030. While Tesla currently stands as the dominant player in the EV market, its landscape is gradually shifting with the recent influx of competition from both EV startups and established automakers launching new EV models.
According to a research firm, Cox Automotive, Tesla accounted for 49.7% of electric vehicles sales in the US.in Q2’2024, down from 59.3% percent a year earlier. In June 2023, Bank of America predicted that that Tesla’s U.S. EV market share could dwindle to just 18% by 2026, after a notable decline from 65% in 2022 to 55% in 2023.
How’s Tesla Responding to the Price War in EV Space?
Tesla has responded to the ongoing price war in the electric vehicle market through a combination of strategies aimed at maintaining its competitive edge and market position. In April 2024, the company announced price cuts for the popular Model Y, as well as the older Model X and Model S in the U.S. market. Following this move, a series of price reductions were introduced in regions including Europe, the Middle East, Asia, and Africa. Investors are also eagerly anticipating the launch of Tesla’s more affordable EV, known as the Model 2, that is expected to launch in 2025.
In 2023, Elon Musk claimed, that the forthcoming vehicle would be approximately half the cost of the Model 3 and Model Y platform, with a speculated starting price of $25,000 (£20,250). This move is poised to expand Tesla’s market share, presenting a formidable competitor to European-manufactured electric hatchbacks such as the Volkswagen ID.3 and models from Chinese brands like MG and BYD.
In other developments, Tesla has officially halted its Gigafactory Mexico project due to concerns over a potential victory for former President and current Republican candidate Donald Trump in the election. Donald Trump has clearly stated that he plans to put tariffs on vehicles built in Mexico and coming into the US, which could significantly impact the company’s profitability.
Elon Musk has also unveiled plans for the introduction of “Optimus,” a humanoid robot expected to commence operations within Tesla factories in 2025 and potentially be available for sale by 2026. Additionally, he has stated that the company’s “Full Self-Driving” system is anticipated to operate without human supervision by the end of 2024, although current testing requires human drivers to be prepared for intervention at all times.
Tesla currently provides two variants of driver-assistance software for its current vehicle lineup. One is known as Autopilot, while the other, a more sophisticated choice, is promoted as Full Self-Driving and is available for a monthly fee of $99. Analysts suggest that these systems could serve as significant revenue streams for the company.
Moreover, Tesla is actively positioning itself in the realm of artificial intelligence, with a focus on autonomous vehicles and the development of driverless taxis, or robotaxis, as a key component of its future endeavors. The company would launch its robotaxi on October 10, that was originally planned for August 08. He believes to easily secure regulatory approval for these robotaxis to put them on roads. His vision extends beyond the autonomous capabilities of the vehicle; he envisions Tesla owners having the opportunity to earn income while they are asleep or at work by allowing the company to utilize their cars as robotaxis. He describes it as “Airbnb on Wheels”.
Conclusion
Despite the decline in electric car sales, Tesla remains bullish on its driverless taxis and artificial intelligence. The company faces the dual challenge of market dynamics and internal restructuring as it strives to retain its position as an industry leader. It will be intriguing to see whether the company’s strategic focus on Full Self-Driving (FSD) and robotaxis, coupled with the introduction of more affordable vehicles, will propel its valuation beyond $1 trillion.
Authored by Ekta Bhatia for Fujn