Introduction
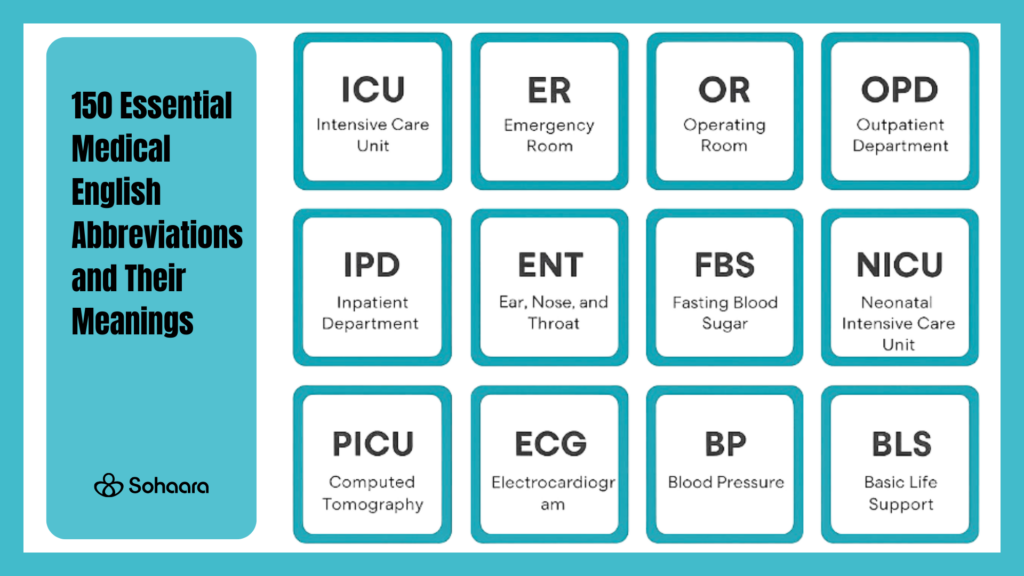
150 Essential Medical English Abbreviations Explained. Learning Medical English can feel overwhelming, especially when every clinical note, patient chart, or hospital report is filled with shortened terms and unfamiliar symbols. Medical abbreviations are a routine part of healthcare communication.
Doctors, nurses, and allied health professionals use these abbreviations to save time and efficiently document patient information. However, for international healthcare professionals, these abbreviations often become one of the biggest barriers to understanding medical texts clearly.
From reading case notes and understanding referral letters to following clinical conversations and writing accurately, abbreviations appear across all sections of the exam. Misunderstanding even a single term can change the meaning of a sentence and affect your overall performance.
In this blog, you’ll find the top 150 high-frequency Medical English abbreviations and their meanings, selected based on real clinical usage. Learning these essential terms will help you communicate in Medical English, write medical reports, avoid confusion, and build confidence for effective exam preparation.
What Are Medical English Abbreviations?
Medical English abbreviations are shortened forms of medical words and phrases commonly used in healthcare settings. They help doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals communicate information quickly and efficiently in patient records, clinical notes, and hospital reports.
These abbreviations represent diagnoses, treatments, investigations, medications, and routine clinical instructions, making documentation faster while maintaining clarity when used correctly.
150 Essential Medical English Abbreviations Explained
Medical English abbreviations are commonly used in clinical notes and healthcare communication. Understanding these terms helps interpret medical information accurately in daily practice. Below is a list of frequently used abbreviations encountered in healthcare settings.
- General Clinical Abbreviations
- Pt — Patient
- Dx — Diagnosis
- Tx — Treatment
- Hx — History
- Rx — Prescription
- Sx — Symptoms
- Px — Prognosis
- C/O — Complains of
- R/O — Rule out
- F/U — Follow-up
- D/C — Discharge / discontinue
- WNL — Within normal limits
- CVA — Cerebrovascular accident (stroke)
- SOB — Shortness of breath
- PMHx — Past medical history
- GI — Gastrointestinal
- MSK — Musculoskeletal
- ENT — Ear, nose, and throat
- LOC — Level of consciousness
- NKDA — No known drug allergies
II. Nursing & Unit Documentation Abbreviations
- ADL — Activities of daily living
- I/O — Intake and output
- PRN — As needed
- NPO — Nothing by mouth
- OOB — Out of bed
- V/S — Vital signs
- EOB — Edge of bed
- ROM — Range of motion
- IVF — Intravenous fluids
- MAR — Medication administration record
- TID — Three times a day
- BID — Twice a day
- SBAR — Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation
- TPR — Temperature, pulse, respirations
- PCA — Patient-controlled analgesia
- PEG — Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
- Foley — Indwelling urinary catheter (US-preferred term)
- CNA — Certified nursing assistant
- DNR — Do not resuscitate
- EWS — Early warning score
III. Vital Signs & Monitoring Abbreviations
- BP — Blood pressure
- HR — Heart rate
- RR — Respiratory rate
- Temp — Temperature
- SpO₂ — Oxygen saturation
- BMI — Body mass index
- GCS — Glasgow Coma Scale
- PEFR — Peak expiratory flow rate
- MAP — Mean arterial pressure
- ECG — Electrocardiogram
- CRT — Capillary refill time
- NEWS — National Early Warning Score
- PaO₂ — Partial pressure of oxygen
- PaCO₂ — Partial pressure of carbon dioxide
- ABG — Arterial blood gas
- ICP — Intracranial pressure
- CVP — Central venous pressure
- ETCO₂ — End-tidal carbon dioxide
- FiO₂ — Fraction of inspired oxygen
- SVR — Systemic vascular resistance
IV. Medication & Treatment Abbreviations
- PO — By mouth (oral)
- IV — Intravenous
- IM — Intramuscular
- SC — Subcutaneous
- STAT — Immediately
- QD — Once daily (US-preferred over OD)
- QID — Four times a day
- HS — At bedtime
- AC — Before meals
- PC — After meals
- NTG — Nitroglycerin (US term instead of GTN)
- NSAID — Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- PPI — Proton pump inhibitor
- TID — Three times daily
- SL — Sublingual
- TPN — Total parenteral nutrition
- IV infusion — Intravenous infusion
- ADR — Adverse drug reaction
- CIVI — Continuous intravenous infusion
- PR — Per rectum
V. Laboratory & Diagnostic Abbreviations
- CBC — Complete blood count
- ESR — Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- CRP — C-reactive protein
- BG — Blood glucose
- UA — Urinalysis
- TSH — Thyroid-stimulating hormone
- LFT — Liver function test
- RFT — Renal function test
- HbA1c — Hemoglobin A1c
- PT — Prothrombin time
- INR — International normalized ratio
- US — Ultrasound
- DEXA — Bone density scan
- ANA — Antinuclear antibody
- D-dimer — Fibrin degradation product
- CK-MB — Creatine kinase–MB
- Troponin T — Cardiac biomarker
- PFT — Pulmonary function test
- ELISA — Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- PCR — Polymerase chain reaction
VI. Emergency & Hospital Department Abbreviations
- ER — Emergency room
- ICU — Intensive care unit
- OPD — Outpatient department
- OR — Operating room
- IP — Inpatient
- EMS — Emergency medical services
- HDU — High-dependency unit
- PACU — Post-anesthesia care unit
- Triage — Patient prioritization based on urgency
- RRT — Rapid response team
- ALS — Advanced life support
- BLS — Basic life support
- MCI — Mass casualty incident
- ATLS — Advanced Trauma Life Support
- FAST — Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma
- Code Blue — Cardiac arrest emergency
- ED LOS — Emergency department length of stay
- RT — Respiratory therapy
- EMT — Emergency medical technician
- C-Spine — Cervical spine
Common Medical Abbreviations Candidates Should Avoid Using
Certain medical abbreviations are considered unclear or unsafe due to their potential for misinterpretation. Using such abbreviations can lead to confusion in clinical communication and documentation. The following are commonly discouraged medical abbreviations in healthcare settings.
- ASAP — As soon as possible
- YO — Years old
- QD — Every day
- QOD — Every other day
- AM — Morning
- PM — Evening
- HxHx — History of history
- DOB — Date of birth
- W/ — With
- W/O — Without
- MS — Morphine sulfate / multiple sclerosis (ambiguous)
- IU — International units (can be misread)
- U — Unit (easily mistaken for zero)
- cc — Cubic centimeters
- MgSO₄ — Magnesium sulfate (can be confused)
- NaCl — Sodium chloride (should be written clearly)
- HSN — At bedtime nightly (unclear usage)
- ODD — Oppositional defiant disorder / odd (confusing)
- TFT — Thyroid function test
- SATS — Oxygen saturation
- APAP — Acetaminophen
- MTX — Methotrexate
- AZT — Zidovudine
- INH — Isoniazid
- 5-FU — Fluorouracil
- CXR — Chest X-ray
- KCl — Potassium chloride
- Mg — Magnesium / milligram (ambiguous)
- q.h. — Every hour
- TIW — Three times a week
Conclusion
Medical English abbreviations allow professionals to record and exchange information efficiently in fast-paced clinical environments. Their use reflects how modern healthcare balances accuracy with time-sensitive decision-making. When understood correctly, abbreviations support clearer interpretation of medical records, smoother handovers, and consistent documentation across teams.
However, their meaning always depends on context, making proper understanding essential for safe communication. Developing familiarity with commonly used abbreviations strengthens overall medical language comprehension, helps write medical reports and notes, and supports effective interaction within healthcare settings.
Want to Learn Medical English? Get Started with Sohaara
Sohaara is an upskilling and networking ecosystem that helps learners and professionals acquire skills and connect with peers, experts, and industry resources while working. The platform offers a range of skills-focused programs, including English for work, communication training, and specialized English tracks that support language development for careers in fields such as healthcare and beyond.
Users can access courses, participate in live sessions, create professional profiles, and engage with a global community that supports skill development from foundational language to advanced workplace communication. With native English facilitators and thoughtfully curated content, Sohaara’s Medical English learning course helps learners feel confident using Medical English in professional scenarios while also tapping into broader career growth tools like job connections, mentoring, and industry networking.
FAQs on Medical English
Why are medical abbreviations used in healthcare?
Medical abbreviations are used to save time and space in fast-paced clinical environments. They help healthcare professionals document information quickly during patient care. Abbreviations also support efficient communication when used consistently and correctly. Their use is common in charts, reports, and clinical notes.
Are medical abbreviations the same worldwide?
No, medical abbreviations can vary by country, healthcare system, and institution. Some abbreviations are widely recognized, while others are local or region-specific. Differences in training and documentation standards also affect usage. This is why context is always important.
Can medical abbreviations have more than one meaning?
Yes, many medical abbreviations can represent multiple terms. Their meaning depends on the clinical context in which they are used. Misinterpretation can occur if the context is unclear. This is one reason caution is required in documentation.
Are medical abbreviations safe to use in patient documentation?
Medical abbreviations are safe when they are standardized and clearly understood. Problems arise when non-approved or ambiguous abbreviations are used. Healthcare facilities often follow approved abbreviation lists. Proper usage helps maintain clarity and patient safety.
What are “unsafe medical abbreviations”?
Unsafe medical abbreviations are terms known to cause confusion or medical errors. They may look similar to other abbreviations or numbers when handwritten. Many healthcare organizations maintain “do not use” lists. These abbreviations are avoided to reduce risk.
Should medical abbreviations be avoided in formal reports?
In formal reports, full medical terms are usually preferred, especially at first mention. Abbreviations may be used later if clearly defined. This ensures accuracy and prevents misunderstanding. Clear documentation is prioritized over speed in formal writing.
Are abbreviations used in verbal communication as well?
Yes, abbreviations are commonly used during verbal communication among healthcare professionals. They are often spoken as letters or shortened terms. Usage depends on familiarity and context. Clear pronunciation is important to avoid miscommunication.
What is the difference between abbreviations and acronyms?
An abbreviation is a shortened form of a word or phrase. An acronym is a type of abbreviation pronounced as a word. For example, “ECG” is spoken letter by letter, while “NATO” is pronounced as a word. Both are used in medical language.
Why is learning medical abbreviations important for healthcare professionals?
Understanding medical abbreviations helps professionals read and interpret clinical information accurately. It supports effective communication within healthcare teams. Familiarity also reduces errors in documentation. This knowledge is essential in everyday clinical practice.